Deploy LLM to Production with HuggingFace Inference Endpoints
How to deploy a fine-tuned Falcon 7B1 LLM with QLoRA to production?
After training Falcon 7B with QLoRA on a custom dataset2, the next step is deploying the model to production. In this tutorial, we’ll utilize HuggingFace Inference Endpoints3 to deploy the model behind a REST API.
Join the AI BootCamp!
Ready to dive into the world of AI and Machine Learning? Join the AI BootCamp to transform your career with the latest skills and hands-on project experience. Learn about LLMs, ML best practices, and much more!
To deploy our model, we’ll merge the fine-tuned QLoRA adapter with the base Falcon 7b model. Next, we’ll upload the combined model, along with the original tokenizer and necessary supporting files, to the HuggingFace Hub. We’ll also include a custom handler to facilitate the inference process.
Finally, we’ll test the API by making a simple call using the requests library. Let’s get started!
In this part, we will be using Jupyter Notebook to run the code. If you prefer to follow along, you can find the notebook on GitHub: GitHub Repository
Setup
Let’s start by installing the required libraries:
!pip install -Uqqq pip --progress-bar off
!pip install -qqq bitsandbytes==0.39.0 --progress-bar off
!pip install -qqq torch==2.0.1 --progress-bar off
!pip install -qqq transformers==4.30.2 --progress-bar off
!pip install -qqq accelerate==0.20.3 --progress-bar off
!pip install -qqq -U git+https://github.com/huggingface/peft.git --progress-bar off
!pip install -qqq datasets==2.12.0 --progress-bar off
!pip install -qqq loralib==0.1.1 --progress-bar off
!pip install -qqq einops==0.6.1 --progress-bar offTo authenticate with the HuggingFace Hub, we’ll need to login using our API token. You can find your token on the HuggingFace profile page :
import torch
import requests
from huggingface_hub import notebook_login
from peft import PeftConfig, PeftModel
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, BitsAndBytesConfig
notebook_login()The Jupyter notebook for this tutorial was executed on a Google Colab instance equipped with an Nvidia T4 GPU (16GB VRAM) and High Memory option.
Merge QLoRA Adapter with Base Model
So far, we have a base model and a QLoRA adapter. Deploying them separately can
be cumbersome as it requires managing files for both the model and the adapter.
Fortunately, the PEFT4 library offers a convenient solution. By calling the
merge_and_unload()5 method on your PEFT model, you can merge the adapter
with the base model.
Let’s start by loading the model:
dtype = torch.bfloat16 if torch.cuda.get_device_capability()[0] == 8 else torch.float16
MODEL_ID = "curiousily/falcon-7b-qlora-chat-support-bot-faq"
config = PeftConfig.from_pretrained(MODEL_ID)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
config.base_model_name_or_path,
return_dict=True,
device_map="auto",
torch_dtype=dtype,
trust_remote_code=True,
)
model = PeftModel.from_pretrained(model, MODEL_ID)
modelPeftModelForCausalLM(
(base_model): LoraModel(
(model): RWForCausalLM(
(transformer): RWModel(
(word_embeddings): Embedding(65024, 4544)
(h): ModuleList(
(0-31): 32 x DecoderLayer(
(input_layernorm): LayerNorm((4544,), eps=1e-05, elementwise_affine=True)
(self_attention): Attention(
(maybe_rotary): RotaryEmbedding()
(query_key_value): Linear(
in_features=4544, out_features=4672, bias=False
(lora_dropout): ModuleDict(
(default): Dropout(p=0.05, inplace=False)
)
(lora_A): ModuleDict(
(default): Linear(in_features=4544, out_features=16, bias=False)
)
(lora_B): ModuleDict(
(default): Linear(in_features=16, out_features=4672, bias=False)
)
(lora_embedding_A): ParameterDict()
(lora_embedding_B): ParameterDict()
)
(dense): Linear(in_features=4544, out_features=4544, bias=False)
(attention_dropout): Dropout(p=0.0, inplace=False)
)
(mlp): MLP(
(dense_h_to_4h): Linear(in_features=4544, out_features=18176, bias=False)
(act): GELU(approximate='none')
(dense_4h_to_h): Linear(in_features=18176, out_features=4544, bias=False)
)
)
)
(ln_f): LayerNorm((4544,), eps=1e-05, elementwise_affine=True)
)
(lm_head): Linear(in_features=4544, out_features=65024, bias=False)
)
)
)Note the LoraModel wrapper. It’s a custom wrapper that allows us to use the
model with the PEFT library. Using float16 to load the model is important as
it allows us to use the model on GPUs with less GPU memory (T4 in our case).
We’ll need to remove it before uploading the model to the HuggingFace Hub:
model = model.merge_and_unload()
modelRWForCausalLM(
(transformer): RWModel(
(word_embeddings): Embedding(65024, 4544)
(h): ModuleList(
(0-31): 32 x DecoderLayer(
(input_layernorm): LayerNorm((4544,), eps=1e-05, elementwise_affine=True)
(self_attention): Attention(
(maybe_rotary): RotaryEmbedding()
(query_key_value): Linear(in_features=4544, out_features=4672, bias=False)
(dense): Linear(in_features=4544, out_features=4544, bias=False)
(attention_dropout): Dropout(p=0.0, inplace=False)
)
(mlp): MLP(
(dense_h_to_4h): Linear(in_features=4544, out_features=18176, bias=False)
(act): GELU(approximate='none')
(dense_4h_to_h): Linear(in_features=18176, out_features=4544, bias=False)
)
)
)
(ln_f): LayerNorm((4544,), eps=1e-05, elementwise_affine=True)
)
(lm_head): Linear(in_features=4544, out_features=65024, bias=False)
)The resulting model has the LoraModel layer removed. The merge_and_unload()
method merges the LoRa layers into the base model by creating new modules
(either an nn.Embedding or an nn.Linear) and replacing the target modules
Push Model to HuggingFace Hub
We’re now prepared to upload our model and tokenizer to the HuggingFace Hub. We’ll begin with the model:
model.push_to_hub(
"curiousily/falcon-7b-qlora-chat-support-bot-faq-merged", use_auth_token=True
)Although we haven’t made any modifications to the tokenizer, we’ll still upload it for ease of use:
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("tiiuae/falcon-7b")
tokenizer.push_to_hub(
"curiousily/falcon-7b-qlora-chat-support-bot-faq-merged", use_auth_token=True
)Unfortunately, the config.json file currently refers to classes in the
original Falcon 7B repository. To resolve this issue, we need to make some
changes to the file and then upload the corresponding supporting files.
Here is the updated version of the config file:
{
"_name_or_path": "tiiuae/falcon-7b",
"alibi": false,
"apply_residual_connection_post_layernorm": false,
"architectures": ["RWForCausalLM"],
"attention_dropout": 0.0,
"auto_map": {
"AutoConfig": "configuration_RW.RWConfig",
"AutoModel": "modelling_RW.RWModel",
"AutoModelForSequenceClassification": "modelling_RW.RWForSequenceClassification",
"AutoModelForTokenClassification": "modelling_RW.RWForTokenClassification",
"AutoModelForQuestionAnswering": "modelling_RW.RWForQuestionAnswering",
"AutoModelForCausalLM": "modelling_RW.RWForCausalLM"
},
"bias": false,
"bos_token_id": 11,
"eos_token_id": 11,
"hidden_dropout": 0.0,
"hidden_size": 4544,
"initializer_range": 0.02,
"layer_norm_epsilon": 1e-5,
"model_type": "RefinedWebModel",
"multi_query": true,
"n_head": 71,
"n_layer": 32,
"parallel_attn": true,
"torch_dtype": "float16",
"transformers_version": "4.30.2",
"use_cache": true,
"vocab_size": 65024
}You also need to upload the files (configuration_RW.py and modelling_RW.py)
from the Supporting Files section.
Inference
You’re now prepared to test your fine-tuned merged model. It loads in the same way as a regular model from the HuggingFace Hub.
model = "curiousily/falcon-7b-qlora-chat-support-bot-faq-merged"
dtype = torch.bfloat16 if torch.cuda.get_device_capability()[0] == 8 else torch.float16
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model,
return_dict=True,
device_map="auto",
load_in_8bit=True,
torch_dtype=dtype,
trust_remote_code=True,
)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model, trust_remote_code=True)You can even wrap it in a text-generation pipeline:
pipeline = transformers.pipeline(
"text-generation",
model=model,
tokenizer=tokenizer,
)Next, define the generation configuration:
generation_config = model.generation_config
generation_config.max_new_tokens = 60
generation_config.temperature = 0
generation_config.num_return_sequences = 1
generation_config.pad_token_id = tokenizer.eos_token_id
generation_config.eos_token_id = tokenizer.eos_token_idFinally, pass a prompt to the model using the pipeline and generation configuration:
prompt = f"""
<human>: How can I create an account?
<assistant>:
""".strip()
result = pipeline(
prompt,
generation_config=generation_config,
)
result[
{
"generated_text": "<human>: How can I create an account?\n<assistant>: To create an account, click the 'Sign Up' button on the top right corner of our website and fill out the registration form with your details. Once you complete the form, you will receive an email with a verification link. Click on the link to confirm your account and start shopping.\n"
}
]The default behavior of the text-generation pipeline is to return a list of
generations (with generated_text).
Here’s another (readable) version of the result:
<human>: How can I create an account?
<assistant>: To create an account, click the 'Sign Up' button on the top right
corner of our website and fill out the registration form with your details.
Once you complete the form, you will receive an email with a verification link.
Click on the link to confirm your account and start shopping.Endpoint Handler
Custom Handlers5 in Hugging Face Endpoints allow you to extend the
functionality of your models by implementing custom pre-processing and
post-processing tasks. By creating a handler.py file in your model repository
on the Hugging Face Hub and implementing the EndpointHandler class, you can
customize the behavior of your models. If you require additional dependencies,
make sure to list them in the requirements.txt file.
Let’s have a look at the handler.py file for our model:
from typing import Any, Dict, List
import torch
import transformers
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
dtype = torch.bfloat16 if torch.cuda.get_device_capability()[0] == 8 else torch.float16
class EndpointHandler:
def __init__(self, path=""):
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(path, trust_remote_code=True)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
path,
return_dict=True,
device_map="auto",
load_in_8bit=True,
torch_dtype=dtype,
trust_remote_code=True,
)
generation_config = model.generation_config
generation_config.max_new_tokens = 60
generation_config.temperature = 0
generation_config.num_return_sequences = 1
generation_config.pad_token_id = tokenizer.eos_token_id
generation_config.eos_token_id = tokenizer.eos_token_id
self.generation_config = generation_config
self.pipeline = transformers.pipeline(
"text-generation", model=model, tokenizer=tokenizer
)
def __call__(self, data: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]:
prompt = data.pop("inputs", data)
result = self.pipeline(prompt, generation_config=self.generation_config)
return resultThe handler’s main task is to initialize a text-generation pipeline using our
model and tokenizer, and then extract the prompt from the input data to generate
a JSON response.
Let’s test it locally:
MODEL_ID = "curiousily/falcon-7b-qlora-chat-support-bot-faq-merged"
my_handler = EndpointHandler(path=MODEL_ID)
prompt = f"""
<human>: How can I create an account?
<assistant>:
""".strip()
payload = {"inputs": prompt}
prediction = my_handler(payload)
prediction[
{
"generated_text": "<human>: How can I create an account?\n<assistant>: To create an account, click the 'Sign Up' button on the top right corner of our website and fill out the registration form. Once you complete the form and submit it, you will receive an email with instructions on how to activate your account.\nIf you encounter any issues during the registration"
}
]The response is the same as the one we got when using the text-generation
pipeline directly.
To deploy the model on Inference Endpoints, we need to create a
requirements.txt file with the dependencies:
torch==2.0.1
transformers==4.30.2
bitsandbytes==0.39.0
accelerate==0.20.3
loralib==0.1.1
einops==0.6.1Deploy the Model on Inference Endpoints
Our model files are now available on the Hugging Face Hub: https://huggingface.co/curiousily/falcon-7b-qlora-chat-support-bot-faq-merged
To start the deploy process, click on the Deploy button:
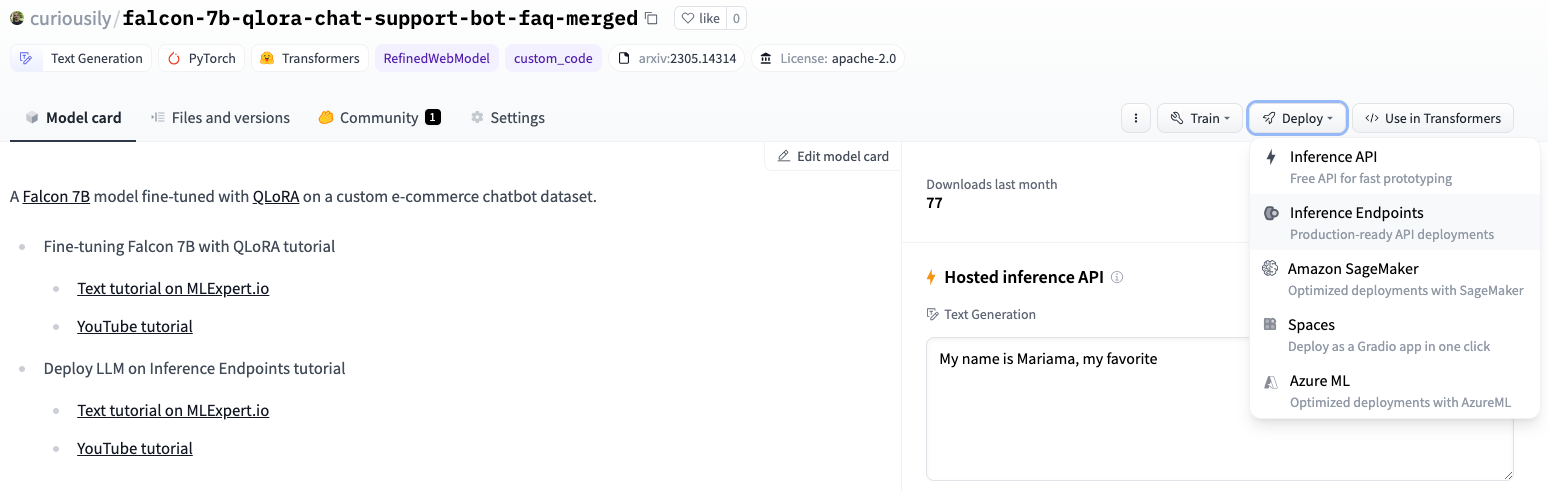
And select the Inference Endpoint option. You’ll be presented with this screen:
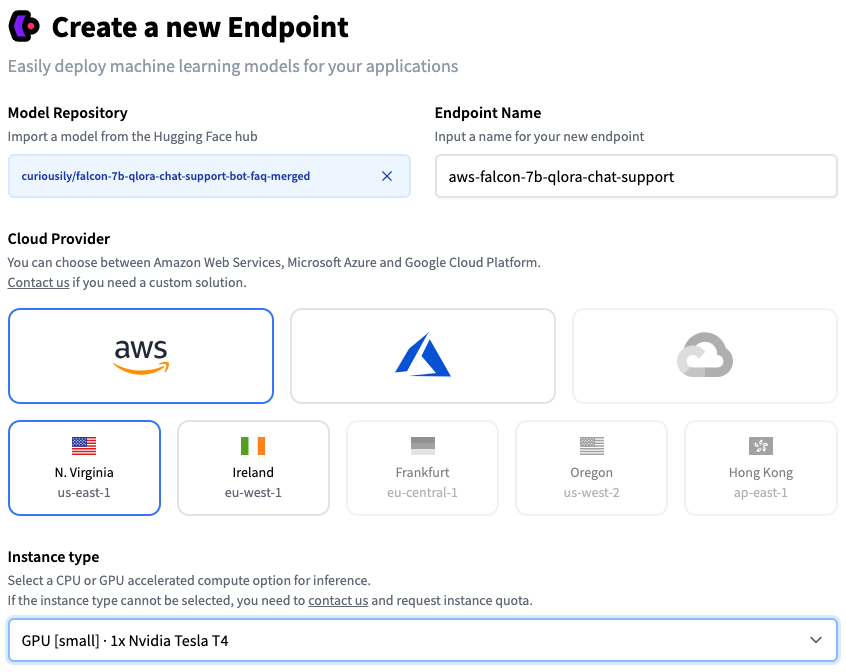
Make sure to select GPU [small] as Instance Type (of course, you can choose a beafier instance if you want to). You can also choose the number of instances you want to deploy. For this tutorial, we’ll stick to a single instance.
Here’re the advanced configuration options:
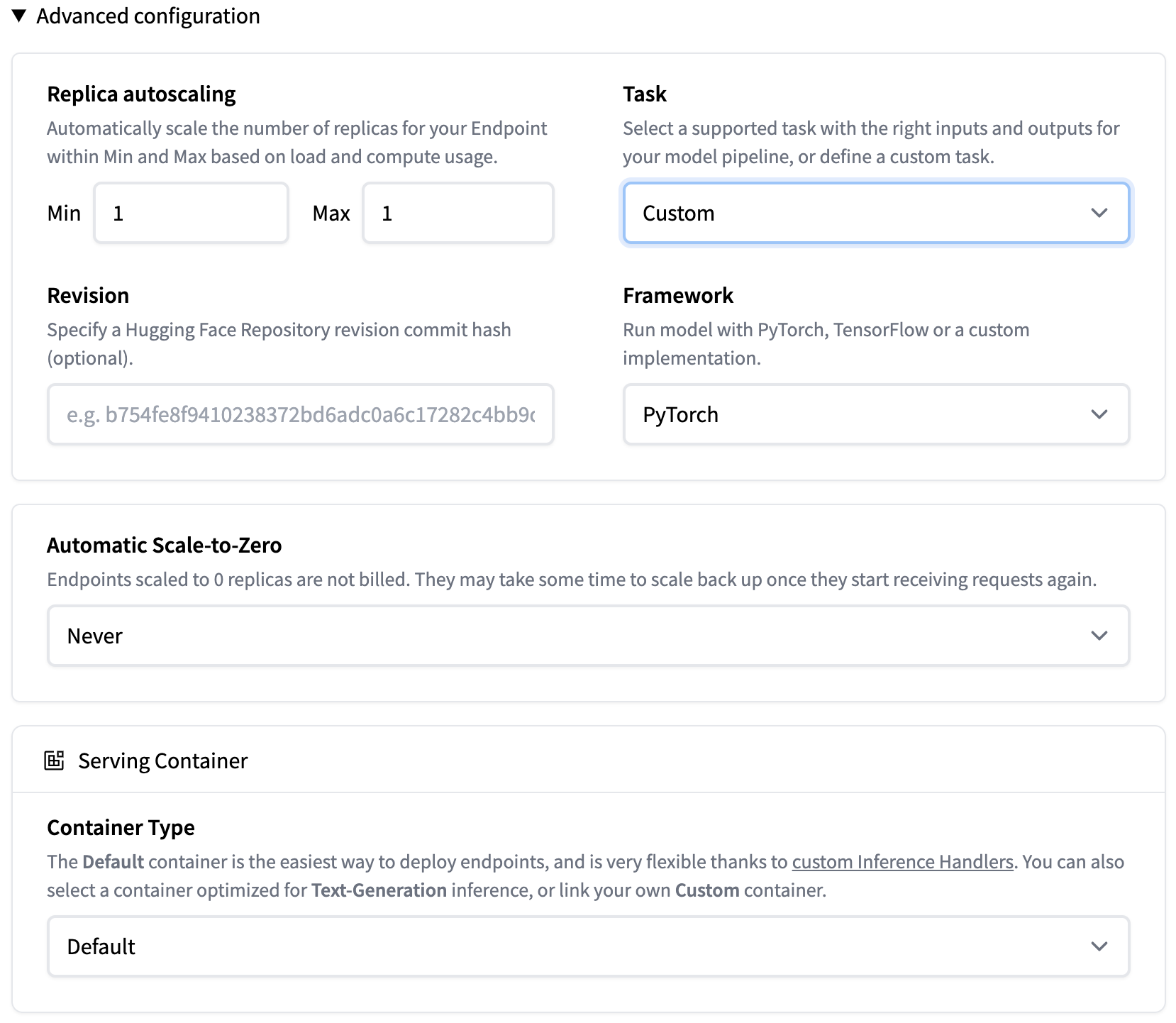
Note that the Task is set to Custom and Container Type is Default
(this allows us to add the custom handler).
After you’re done with the configuration, click on the Create Endpoint button. This will start the deployment process (might take a few minutes). Once everything is running, you should be able to get the endpoint URL:
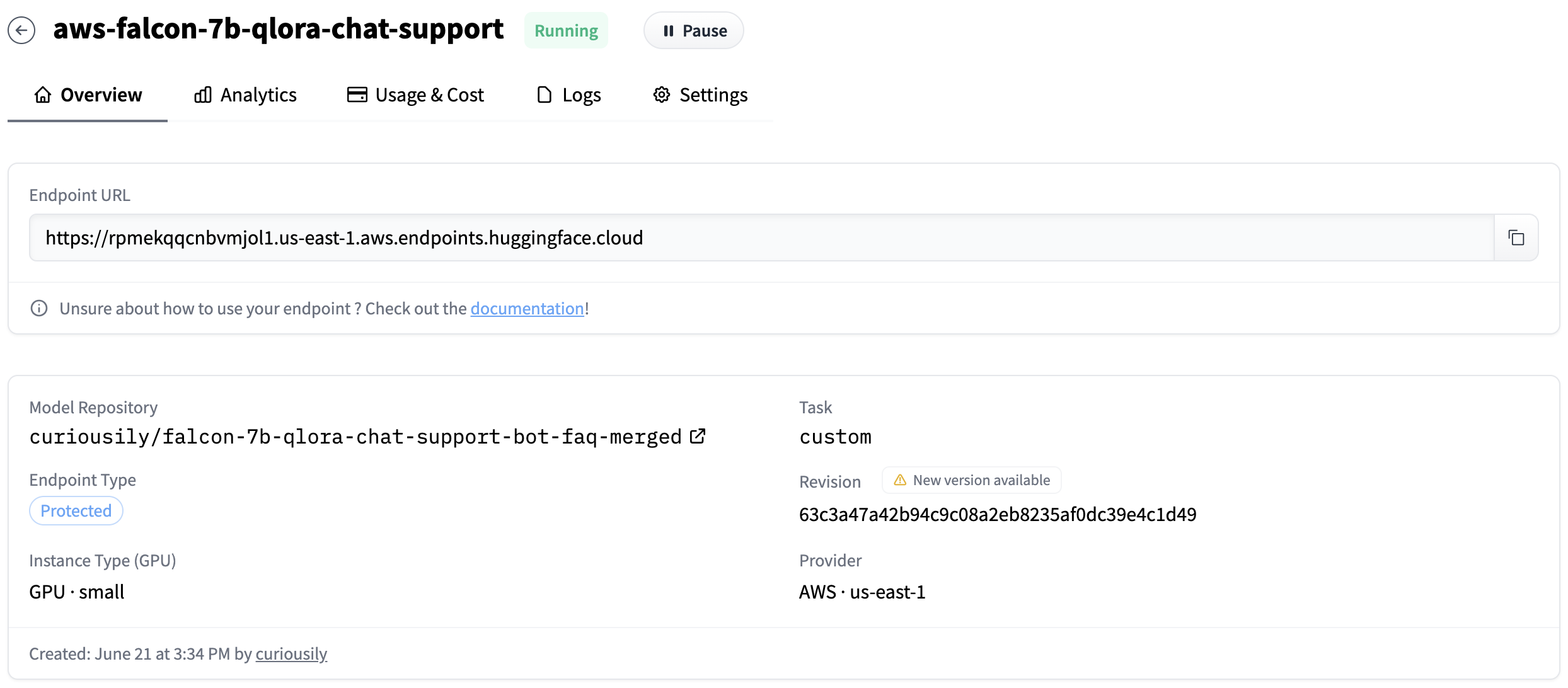
Test the API
Once everything is running and the endpoint is ready, we can test it using a
POST request with library like requests:
API_URL = "YOUR_ENDPOINT_URL"
API_TOKEN = "YOUR_HUGGINGFACE_TOKEN"
headers = {"Authorization": f"Bearer {API_TOKEN}"}
prompt = f"""
<human>: How can I create an account?
<assistant>:
""".strip()
payload = {"inputs": prompt}
response = requests.post(API_URL, json=payload, headers=headers)
response = resp.json()
response[
{
"generated_text": "<human>: How can I create an account?\n<assistant>: To create an account, click the 'Sign Up' button on the top right corner of our website and fill out the registration form. Once you complete the form and submit it, you will receive an email with instructions on how to activate your account.\nIf you encounter any issues during the registration"
}
]The code snippet defines the API URL and token, creates headers with the authorization token, and prepares the prompt for the conversation. The prompt is then sent as a JSON payload in a POST request to the API URL. The response is a JSON object with the generated text.
Let’s look at the generated text:
print(response[0]["generated_text"])<human>: How can I create an account?
<assistant>: To create an account, click the 'Sign Up' button on the top right
corner of our website and fill out the registration form. Once you complete the
form and submit it, you will receive an email with instructions on how to
activate your account.
If you encounter any issues during the registrationSupporting Files
configuration_RW.py
# coding=utf-8
# Copyright 2022 the Big Science Workshop and HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
""" Bloom configuration"""
from transformers.configuration_utils import PretrainedConfig
from transformers.utils import logging
logger = logging.get_logger(__name__)
class RWConfig(PretrainedConfig):
model_type = "RefinedWebModel"
keys_to_ignore_at_inference = ["past_key_values"]
attribute_map = {
"num_hidden_layers": "n_layer",
"num_attention_heads": "n_head",
}
def __init__(
self,
vocab_size=250880,
hidden_size=64,
n_layer=2,
n_head=8,
layer_norm_epsilon=1e-5,
initializer_range=0.02,
use_cache=True,
bos_token_id=1,
eos_token_id=2,
apply_residual_connection_post_layernorm=False,
hidden_dropout=0.0,
attention_dropout=0.0,
multi_query=False,
alibi=False,
bias=False,
parallel_attn=False,
**kwargs,
):
self.vocab_size = vocab_size
# Backward compatibility with n_embed kwarg
n_embed = kwargs.pop("n_embed", None)
self.hidden_size = hidden_size if n_embed is None else n_embed
self.n_layer = n_layer
self.n_head = n_head
self.layer_norm_epsilon = layer_norm_epsilon
self.initializer_range = initializer_range
self.use_cache = use_cache
self.apply_residual_connection_post_layernorm = apply_residual_connection_post_layernorm
self.hidden_dropout = hidden_dropout
self.attention_dropout = attention_dropout
self.bos_token_id = bos_token_id
self.eos_token_id = eos_token_id
self.multi_query = multi_query
self.alibi = alibi
self.bias = bias
self.parallel_attn = parallel_attn
super().__init__(bos_token_id=bos_token_id, eos_token_id=eos_token_id, **kwargs)
@property
def head_dim(self):
return self.hidden_size // self.n_head
@property
def rotary(self):
return not self.alibimodelling_RW.py
# port of models described in RW
# We use the bloom model as a starting point for these model.
# Please refer to the bloom models for usage instructions.
import math
import warnings
from typing import Optional, Tuple, Union
import torch
import torch.utils.checkpoint
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import BCEWithLogitsLoss, CrossEntropyLoss, LayerNorm, MSELoss
from torch.nn import functional as F
from transformers.modeling_outputs import (
BaseModelOutputWithPastAndCrossAttentions,
CausalLMOutputWithCrossAttentions,
QuestionAnsweringModelOutput,
SequenceClassifierOutputWithPast,
TokenClassifierOutput,
)
from transformers.modeling_utils import PreTrainedModel
from transformers.utils import logging
from .configuration_RW import RWConfig
logger = logging.get_logger(__name__)
# NOTE(Hesslow): Unfortunately we did not fuse matmul and bias during training, this means that there's one additional quantization to bfloat16 between the operations.
# In order not to degrade the quality of our HF-port, we keep these characteristics in the final model.
class Linear(nn.Linear):
def forward(self, input: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
ret = input @ self.weight.T
if self.bias is None:
return ret
else:
return ret + self.bias
from einops import rearrange
# rotary pos emb helpers (torch.jit.script does not seem to support staticmethod...)
def rotate_half(x):
x1, x2 = x[..., : x.shape[-1] // 2], x[..., x.shape[-1] // 2 :]
return torch.cat((-x2, x1), dim=x1.ndim - 1) # dim=-1 triggers a bug in torch < 1.8.0
class RotaryEmbedding(torch.nn.Module):
"""Implementation of RotaryEmbedding from GPT-NeoX.
This implementation is design to operate on queries and keys that are compatible with
[batch_size, n_heads_per_partition, seq_len, head_dim] (e.g. MinGPTAttention format).
"""
def __init__(
self,
head_dim: int,
base=10000,
):
super().__init__()
inv_freq = 1.0 / (base ** (torch.arange(0, head_dim, 2).float() / head_dim))
self.register_buffer("inv_freq", inv_freq, persistent=False)
self.head_dim = head_dim
self.seq_len_cached = None
self.batch_size_cached = None
self.cos_cached: torch.Tensor | None = None
self.sin_cached: torch.Tensor | None = None
def cos_sin(
self,
seq_len: int,
device="cuda",
dtype=torch.bfloat16,
) -> torch.Tensor:
if seq_len != self.seq_len_cached:
self.seq_len_cached = seq_len
t = torch.arange(seq_len, device=device).type_as(self.inv_freq)
freqs = torch.einsum("i,j->ij", t, self.inv_freq)
emb = torch.cat((freqs, freqs), dim=-1).to(device)
if dtype in [torch.float16, torch.bfloat16]:
emb = emb.float()
self.cos_cached = emb.cos()[None, :, :]
self.sin_cached = emb.sin()[None, :, :]
self.cos_cached = self.cos_cached.type(dtype)
self.sin_cached = self.sin_cached.type(dtype)
return self.cos_cached, self.sin_cached
def forward(self, q, k):
batch, seq_len, head_dim = q.shape
cos, sin = self.cos_sin(seq_len, q.device, q.dtype)
return (q * cos) + (rotate_half(q) * sin), (k * cos) + (rotate_half(k) * sin)
def _make_causal_mask(
input_ids_shape: torch.Size, device: torch.device, past_key_values_length: int
) -> torch.BoolTensor:
batch_size, target_length = input_ids_shape
mask = torch.empty((target_length, target_length + past_key_values_length), dtype=torch.bool, device=device)
# ONNX doesn't support `torch.Tensor.triu` properly, thus we use this workaround
seq_ids = torch.arange(target_length, device=device)
mask[:, past_key_values_length:] = seq_ids[:, None] < seq_ids[None, :]
if past_key_values_length > 0:
mask[:, :past_key_values_length] = False
expanded_mask = mask[None, None, :, :].expand(batch_size, 1, target_length, target_length + past_key_values_length)
return expanded_mask
def _expand_mask(mask: torch.Tensor, tgt_length: int) -> torch.BoolTensor:
batch_size, src_length = mask.shape
tgt_length = tgt_length if tgt_length is not None else src_length
expanded_mask = ~(mask[:, None, None, :].to(torch.bool))
return expanded_mask.expand(batch_size, 1, tgt_length, src_length)
def build_alibi_tensor(attention_mask: torch.Tensor, num_heads: int, dtype: torch.dtype) -> torch.Tensor:
batch_size, seq_length = attention_mask.shape
closest_power_of_2 = 2 ** math.floor(math.log2(num_heads))
base = torch.tensor(
2 ** (-(2 ** -(math.log2(closest_power_of_2) - 3))), device=attention_mask.device, dtype=torch.float32
)
powers = torch.arange(1, 1 + closest_power_of_2, device=attention_mask.device, dtype=torch.int32)
slopes = torch.pow(base, powers)
if closest_power_of_2 != num_heads:
extra_base = torch.tensor(
2 ** (-(2 ** -(math.log2(2 * closest_power_of_2) - 3))), device=attention_mask.device, dtype=torch.float32
)
num_remaining_heads = min(closest_power_of_2, num_heads - closest_power_of_2)
extra_powers = torch.arange(1, 1 + 2 * num_remaining_heads, 2, device=attention_mask.device, dtype=torch.int32)
slopes = torch.cat([slopes, torch.pow(extra_base, extra_powers)], dim=0)
# Note: alibi will added to the attention bias that will be applied to the query, key product of attention
# => therefore alibi will have to be of shape (batch_size, num_heads, query_length, key_length)
# => here we set (batch_size=1, num_heads=num_heads, query_length=1, key_length=max_length)
# => the query_length dimension will then be broadcasted correctly
# This is more or less identical to T5's relative position bias:
# https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/f681437203baa7671de3174b0fa583c349d9d5e1/src/transformers/models/t5/modeling_t5.py#L527
arange_tensor = ((attention_mask.cumsum(dim=-1) - 1) * attention_mask)[:, None, :]
alibi = slopes[..., None].bfloat16() * arange_tensor
return alibi.reshape(batch_size * num_heads, 1, seq_length).to(dtype)
def dropout_add(x: torch.Tensor, residual: torch.Tensor, prob: float, training: bool) -> torch.Tensor:
out = F.dropout(x, p=prob, training=training)
out = residual + out
return out
class Attention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config: RWConfig):
super().__init__()
self.hidden_size = config.hidden_size
self.num_heads = config.n_head
self.head_dim = self.hidden_size // self.num_heads
self.split_size = self.hidden_size
self.hidden_dropout = config.hidden_dropout
if self.head_dim * self.num_heads != self.hidden_size:
raise ValueError(
f"`hidden_size` must be divisible by num_heads (got `hidden_size`: {self.hidden_size} and `num_heads`:"
f" {self.num_heads})."
)
self.maybe_rotary = RotaryEmbedding(config.head_dim) if config.rotary else lambda q, k: (q, k)
# Layer-wise attention scaling
self.inv_norm_factor = 1.0 / math.sqrt(self.head_dim)
self.beta = self.inv_norm_factor
self.query_key_value = Linear(
self.hidden_size,
3 * self.hidden_size if not config.multi_query else (self.hidden_size + 2 * self.head_dim),
bias=config.bias,
)
self.multi_query = config.multi_query
self.dense = Linear(self.hidden_size, self.hidden_size, bias=config.bias)
self.attention_dropout = nn.Dropout(config.attention_dropout)
self.num_kv = config.n_head if not self.multi_query else 1
def _split_heads(self, fused_qkv: torch.Tensor) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]:
"""
Split the last dimension into (num_heads, head_dim) without making any copies, results share same memory
storage as `fused_qkv`
Args:
fused_qkv (`torch.tensor`, *required*): [batch_size, seq_length, num_heads * 3 * head_dim]
Returns:
query: [batch_size, seq_length, num_heads, head_dim] key: [batch_size, seq_length, num_heads, head_dim]
value: [batch_size, seq_length, num_heads, head_dim]
"""
if not self.multi_query:
batch_size, seq_length, three_times_hidden_size = fused_qkv.shape
fused_qkv = fused_qkv.view(batch_size, seq_length, self.num_heads, 3, self.head_dim)
return fused_qkv[..., 0, :], fused_qkv[..., 1, :], fused_qkv[..., 2, :]
else:
batch_size, seq_length, three_times_hidden_size = fused_qkv.shape
fused_qkv = fused_qkv.view(batch_size, seq_length, self.num_heads + 2, self.head_dim)
return fused_qkv[..., :-2, :], fused_qkv[..., [-2], :], fused_qkv[..., [-1], :]
def _merge_heads(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
"""
Merge heads together over the last dimenstion
Args:
x: (`torch.tensor`, *required*): [batch_size * num_heads, seq_length, head_dim]
Returns:
torch.tensor: [batch_size, seq_length, num_heads * head_dim]
"""
# What we want to achieve is:
# batch_size * num_heads, seq_length, head_dim -> batch_size, seq_length, num_heads * head_dim
batch_size_and_num_heads, seq_length, _ = x.shape
batch_size = batch_size_and_num_heads // self.num_heads
# First view to decompose the batch size
# batch_size * num_heads, seq_length, head_dim -> batch_size, num_heads, seq_length, head_dim
x = x.view(batch_size, self.num_heads, seq_length, self.head_dim)
# batch_size, num_heads, seq_length, head_dim -> batch_size, seq_length, num_heads, head_dim
x = x.permute(0, 2, 1, 3)
# batch_size, seq_length, num_heads, head_dim -> batch_size, seq_length, num_heads * head_dim
return x.reshape(batch_size, seq_length, self.num_heads * self.head_dim)
def forward(
self,
hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
alibi: torch.Tensor,
attention_mask: torch.Tensor,
layer_past: Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]] = None,
head_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
use_cache: bool = False,
output_attentions: bool = False,
):
fused_qkv = self.query_key_value(hidden_states) # [batch_size, seq_length, 3 x hidden_size]
# 3 x [batch_size, seq_length, num_heads, head_dim]
(query_layer, key_layer, value_layer) = self._split_heads(fused_qkv)
batch_size, q_length, _, _ = query_layer.shape
query_layer = query_layer.transpose(1, 2).reshape(batch_size * self.num_heads, q_length, self.head_dim)
key_layer = key_layer.transpose(1, 2).reshape(
batch_size * self.num_kv,
q_length,
self.head_dim,
)
value_layer = value_layer.transpose(1, 2).reshape(batch_size * self.num_kv, q_length, self.head_dim)
query_layer, key_layer = self.maybe_rotary(query_layer, key_layer)
if layer_past is not None:
past_key, past_value = layer_past
# concatenate along seq_length dimension:
# - key: [batch_size * self.num_heads, head_dim, kv_length]
# - value: [batch_size * self.num_heads, kv_length, head_dim]
key_layer = torch.cat((past_key, key_layer), dim=1)
value_layer = torch.cat((past_value, value_layer), dim=1)
_, kv_length, _ = key_layer.shape
if use_cache is True:
present = (key_layer, value_layer)
else:
present = None
if alibi is None:
query_layer_ = query_layer.reshape(batch_size, self.num_heads, -1, self.head_dim)
key_layer_ = key_layer.reshape(batch_size, self.num_kv, -1, self.head_dim)
value_layer_ = value_layer.reshape(batch_size, self.num_kv, -1, self.head_dim)
attn_output = F.scaled_dot_product_attention(
query_layer_, key_layer_, value_layer_, None, 0.0, is_causal=True
)
x = attn_output.view(batch_size, self.num_heads, q_length, self.head_dim)
x = x.permute(0, 2, 1, 3)
attn_output = x.reshape(batch_size, q_length, self.num_heads * self.head_dim)
output_tensor = self.dense(attn_output)
outputs = (output_tensor, present)
assert not output_attentions # not supported.
return outputs
else:
attention_mask_float = (attention_mask * 1.0).masked_fill(attention_mask, -1e9).to(torch.bfloat16)
matmul_result = query_layer @ key_layer.transpose(-1, -2)
# change view to [batch_size, num_heads, q_length, kv_length]
attention_scores = matmul_result.view(batch_size, self.num_heads, q_length, kv_length)
# cast attention scores to fp32, compute scaled softmax and cast back to initial dtype - [batch_size, num_heads, q_length, kv_length]
input_dtype = attention_scores.dtype
# `float16` has a minimum value of -65504.0, whereas `bfloat16` and `float32` have a minimum value of `-3.4e+38`
if input_dtype == torch.float16 or input_dtype == torch.bfloat16:
attention_scores = attention_scores.to(torch.float32)
# attn_weights = torch.masked_fill(attention_scores, attention_mask, torch.finfo(attention_scores.dtype).min)
attention_probs = F.softmax(
(attention_scores + alibi.view(batch_size, self.num_heads, 1, -1)) * self.inv_norm_factor + attention_mask_float,
dim=-1,
dtype=hidden_states.dtype,
)
# [batch_size, num_heads, q_length, kv_length]
attention_probs = self.attention_dropout(attention_probs)
if head_mask is not None:
attention_probs = attention_probs * head_mask
# change view [batch_size x num_heads, q_length, kv_length]
attention_probs_reshaped = attention_probs.view(batch_size * self.num_heads, q_length, kv_length)
# matmul: [batch_size * num_heads, q_length, head_dim]
context_layer = attention_probs_reshaped @ value_layer
# change view [batch_size, num_heads, q_length, head_dim]
context_layer = self._merge_heads(context_layer)
output_tensor = self.dense(context_layer)
outputs = (output_tensor, present)
if output_attentions:
outputs += (attention_probs,)
return outputs
class MLP(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config: RWConfig):
super().__init__()
hidden_size = config.hidden_size
self.dense_h_to_4h = Linear(hidden_size, 4 * hidden_size, bias=config.bias)
self.act = nn.GELU()
self.dense_4h_to_h = Linear(4 * hidden_size, hidden_size, bias=config.bias)
self.hidden_dropout = config.hidden_dropout
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
x = self.act(self.dense_h_to_4h(x))
x = self.dense_4h_to_h(x)
return x
class DecoderLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config: RWConfig):
super().__init__()
hidden_size = config.hidden_size
self.input_layernorm = LayerNorm(hidden_size, eps=config.layer_norm_epsilon)
self.num_heads = config.n_head
self.self_attention = Attention(config)
if not config.parallel_attn:
# unused if parallel attn
self.post_attention_layernorm = LayerNorm(hidden_size, eps=config.layer_norm_epsilon)
self.mlp = MLP(config)
self.apply_residual_connection_post_layernorm = config.apply_residual_connection_post_layernorm
self.hidden_dropout = config.hidden_dropout
self.config = config
def forward(
self,
hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
alibi: torch.Tensor,
attention_mask: torch.Tensor,
layer_past: Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]] = None,
head_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
use_cache: bool = False,
output_attentions: bool = False,
):
layernorm_output = self.input_layernorm(hidden_states)
residual = hidden_states
# Self attention.
attn_outputs = self.self_attention(
layernorm_output,
layer_past=layer_past,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
alibi=alibi,
head_mask=head_mask,
use_cache=use_cache,
output_attentions=output_attentions,
)
attention_output = attn_outputs[0]
if not self.config.parallel_attn:
residual = dropout_add(attention_output, residual, self.config.attention_dropout, training=self.training)
layernorm_output = self.post_attention_layernorm(residual)
outputs = attn_outputs[1:]
# MLP.
mlp_output = self.mlp(layernorm_output)
if self.config.parallel_attn:
mlp_output += attention_output
output = dropout_add(mlp_output, residual, self.config.hidden_dropout, training=self.training)
if use_cache:
outputs = (output,) + outputs
else:
outputs = (output,) + outputs[1:]
return outputs # hidden_states, present, attentions
class RWPreTrainedModel(PreTrainedModel):
_keys_to_ignore_on_load_missing = [r"h.*.self_attention.scale_mask_softmax.causal_mask", r"lm_head.weight"]
"""
An abstract class to handle weights initialization and a simple interface for downloading and loading pretrained
models.
"""
config_class = RWConfig
base_model_prefix = "transformer"
supports_gradient_checkpointing = True
_no_split_modules = ["DecoderLayer"]
def __init__(self, *inputs, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*inputs, **kwargs)
def _init_weights(self, module: nn.Module):
"""Initialize the weights."""
if isinstance(module, nn.Linear) or isinstance(module, Linear):
# Slightly different from the TF version which uses truncated_normal for initialization
# cf https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/5617
module.weight.data.normal_(mean=0.0, std=self.config.initializer_range)
if module.bias is not None:
module.bias.data.zero_()
elif isinstance(module, nn.Embedding):
module.weight.data.normal_(mean=0.0, std=self.config.initializer_range)
if module.padding_idx is not None:
module.weight.data[module.padding_idx].zero_()
elif isinstance(module, LayerNorm):
module.bias.data.zero_()
module.weight.data.fill_(1.0)
def _set_gradient_checkpointing(self, module: nn.Module, value: bool = False):
if isinstance(module, RWModel):
module.gradient_checkpointing = value
@staticmethod
def _convert_to_standard_cache(
past_key_value: Tuple[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]], batch_size: int
) -> Tuple[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]]:
"""
Standardizes the format of the cache so as to match most implementations, i.e. to tuple(tuple([batch_size,
num_heads, ...]))
"""
batch_size_times_num_heads, head_dim, seq_length = past_key_value[0][0].shape
num_heads = batch_size_times_num_heads // batch_size
# key: [batch_size * num_heads, head_dim, seq_length] -> [batch_size, num_heads, head_dim, seq_length]
# value: [batch_size * num_heads, seq_length, head_dim] -> [batch_size, num_heads, seq_length, head_dim]
return tuple(
(
layer_past[0].view(batch_size, num_heads, head_dim, seq_length),
layer_past[1].view(batch_size, num_heads, seq_length, head_dim),
)
for layer_past in past_key_value
)
@staticmethod
def _convert_to_rw_cache(
past_key_value: Tuple[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]]
) -> Tuple[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]]:
batch_size, num_heads, head_dim, seq_length = past_key_value[0][0].shape
batch_size_times_num_heads = batch_size * num_heads
# key: [batch_size, num_heads, head_dim, seq_length] -> [batch_size * num_heads, head_dim, seq_length]
# value: [batch_size, num_heads, seq_length, head_dim] -> [batch_size * num_heads, seq_length, head_dim]
return tuple(
(
layer_past[0].view(batch_size_times_num_heads, head_dim, seq_length),
layer_past[1].view(batch_size_times_num_heads, seq_length, head_dim),
)
for layer_past in past_key_value
)
class RWModel(RWPreTrainedModel):
def __init__(self, config: RWConfig):
super().__init__(config)
self.embed_dim = config.hidden_size
self.num_heads = config.n_head
self.alibi = config.alibi
# Embedding + LN Embedding
self.word_embeddings = nn.Embedding(config.vocab_size, self.embed_dim)
# Transformer blocks
self.h = nn.ModuleList([DecoderLayer(config) for _ in range(config.num_hidden_layers)])
# Final Layer Norm
self.ln_f = LayerNorm(self.embed_dim, eps=config.layer_norm_epsilon)
self.gradient_checkpointing = False
# Initialize weights and apply final processing
self.post_init()
def get_input_embeddings(self):
return self.word_embeddings
def _prepare_attn_mask(
self, attention_mask: torch.Tensor, input_shape: Tuple[int, int], past_key_values_length: int
) -> torch.BoolTensor:
# create causal mask
# [batch_size, seq_length] -> [batch_size, 1, tgt_length, src_length]
combined_attention_mask = None
device = attention_mask.device
_, src_length = input_shape
if src_length > 1:
combined_attention_mask = _make_causal_mask(
input_shape, device=device, past_key_values_length=past_key_values_length
)
# [batch_size, seq_length] -> [batch_size, 1, tgt_length, src_length]
expanded_attn_mask = _expand_mask(attention_mask, tgt_length=src_length)
combined_attention_mask = (
expanded_attn_mask if combined_attention_mask is None else expanded_attn_mask | combined_attention_mask
)
return combined_attention_mask
def set_input_embeddings(self, new_embeddings: torch.Tensor):
self.word_embeddings = new_embeddings
def forward(
self,
input_ids: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
past_key_values: Optional[Tuple[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor], ...]] = None,
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
head_mask: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
inputs_embeds: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
use_cache: Optional[bool] = None,
output_attentions: Optional[bool] = None,
output_hidden_states: Optional[bool] = None,
return_dict: Optional[bool] = None,
**deprecated_arguments,
) -> Union[Tuple[torch.Tensor, ...], BaseModelOutputWithPastAndCrossAttentions]:
if deprecated_arguments.pop("position_ids", False) is not False:
# `position_ids` could have been `torch.Tensor` or `None` so defaulting pop to `False` allows to detect if users were passing explicitly `None`
warnings.warn(
"`position_ids` have no functionality in BLOOM and will be removed in v5.0.0. You can safely ignore"
" passing `position_ids`.",
FutureWarning,
)
if len(deprecated_arguments) > 0:
raise ValueError(f"Got unexpected arguments: {deprecated_arguments}")
output_attentions = output_attentions if output_attentions is not None else self.config.output_attentions
output_hidden_states = (
output_hidden_states if output_hidden_states is not None else self.config.output_hidden_states
)
use_cache = use_cache if use_cache is not None else self.config.use_cache
return_dict = return_dict if return_dict is not None else self.config.use_return_dict
if input_ids is not None and inputs_embeds is not None:
raise ValueError("You cannot specify both input_ids and inputs_embeds at the same time")
elif input_ids is not None:
batch_size, seq_length = input_ids.shape
elif inputs_embeds is not None:
batch_size, seq_length, _ = inputs_embeds.shape
else:
raise ValueError("You have to specify either input_ids or inputs_embeds")
if past_key_values is None:
past_key_values = tuple([None] * len(self.h))
# Prepare head mask if needed
# 1.0 in head_mask indicate we keep the head
# attention_probs has shape batch_size x num_heads x N x N
# head_mask has shape n_layer x batch x num_heads x N x N
head_mask = self.get_head_mask(head_mask, self.config.n_layer)
if inputs_embeds is None:
inputs_embeds = self.word_embeddings(input_ids)
hidden_states = inputs_embeds
presents = () if use_cache else None
all_self_attentions = () if output_attentions else None
all_hidden_states = () if output_hidden_states else None
# Compute alibi tensor: check build_alibi_tensor documentation
seq_length_with_past = seq_length
past_key_values_length = 0
if past_key_values[0] is not None:
past_key_values_length = past_key_values[0][0].shape[2]
seq_length_with_past = seq_length_with_past + past_key_values_length
if attention_mask is None:
attention_mask = torch.ones((batch_size, seq_length_with_past), device=hidden_states.device)
else:
attention_mask = attention_mask.to(hidden_states.device)
if self.alibi:
alibi = build_alibi_tensor(attention_mask, self.num_heads, dtype=hidden_states.dtype)
else:
alibi = None
causal_mask = self._prepare_attn_mask(
attention_mask,
input_shape=(batch_size, seq_length),
past_key_values_length=past_key_values_length,
)
for i, (block, layer_past) in enumerate(zip(self.h, past_key_values)):
if output_hidden_states:
all_hidden_states = all_hidden_states + (hidden_states,)
if self.gradient_checkpointing and self.training:
if use_cache:
logger.warning(
"`use_cache=True` is incompatible with gradient checkpointing. Setting `use_cache=False`..."
)
use_cache = False
def create_custom_forward(module):
def custom_forward(*inputs):
# None for past_key_value
return module(*inputs, use_cache=use_cache, output_attentions=output_attentions)
return custom_forward
outputs = torch.utils.checkpoint.checkpoint(
create_custom_forward(block),
hidden_states,
alibi,
causal_mask,
head_mask[i],
)
else:
outputs = block(
hidden_states,
layer_past=layer_past,
attention_mask=causal_mask,
head_mask=head_mask[i],
use_cache=use_cache,
output_attentions=output_attentions,
alibi=alibi,
)
hidden_states = outputs[0]
if use_cache is True:
presents = presents + (outputs[1],)
if output_attentions:
all_self_attentions = all_self_attentions + (outputs[2 if use_cache else 1],)
# Add last hidden state
hidden_states = self.ln_f(hidden_states)
if output_hidden_states:
all_hidden_states = all_hidden_states + (hidden_states,)
if not return_dict:
return tuple(v for v in [hidden_states, presents, all_hidden_states, all_self_attentions] if v is not None)
return BaseModelOutputWithPastAndCrossAttentions(
last_hidden_state=hidden_states,
past_key_values=presents,
hidden_states=all_hidden_states,
attentions=all_self_attentions,
)
class RWForCausalLM(RWPreTrainedModel):
_keys_to_ignore_on_load_missing = [r"h.*.self_attention.scale_mask_softmax.causal_mask", r"lm_head.weight"]
def __init__(self, config: RWConfig):
super().__init__(config)
self.transformer = RWModel(config)
self.lm_head = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, config.vocab_size, bias=False)
# Initialize weights and apply final processing
self.post_init()
def get_output_embeddings(self):
return self.lm_head
def set_output_embeddings(self, new_embeddings: torch.Tensor):
self.lm_head = new_embeddings
def prepare_inputs_for_generation(
self,
input_ids: torch.LongTensor,
past: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
**kwargs,
) -> dict:
# only last token for input_ids if past is not None
if past:
input_ids = input_ids[:, -1].unsqueeze(-1)
# the cache may be in the stardard format (e.g. in contrastive search), convert to our's format if needed
if past[0][0].shape[0] == input_ids.shape[0]:
past = self._convert_to_rw_cache(past)
return {
"input_ids": input_ids,
"past_key_values": past,
"use_cache": kwargs.get("use_cache"),
"attention_mask": attention_mask,
}
def forward(
self,
input_ids: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
past_key_values: Optional[Tuple[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor], ...]] = None,
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
head_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
inputs_embeds: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
labels: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
use_cache: Optional[bool] = None,
output_attentions: Optional[bool] = None,
output_hidden_states: Optional[bool] = None,
return_dict: Optional[bool] = None,
**deprecated_arguments,
) -> Union[Tuple[torch.Tensor], CausalLMOutputWithCrossAttentions]:
r"""
labels (`torch.LongTensor` of shape `(batch_size, sequence_length)`, *optional*):
Labels for language modeling. Note that the labels **are shifted** inside the model, i.e. you can set
`labels = input_ids` Indices are selected in `[-100, 0, ..., config.vocab_size]` All labels set to `-100`
are ignored (masked), the loss is only computed for labels in `[0, ..., config.vocab_size]`
"""
if deprecated_arguments.pop("position_ids", False) is not False:
# `position_ids` could have been `torch.Tensor` or `None` so defaulting pop to `False` allows to detect if users were passing explicitly `None`
warnings.warn(
"`position_ids` have no functionality in BLOOM and will be removed in v5.0.0. You can safely ignore"
" passing `position_ids`.",
FutureWarning,
)
if len(deprecated_arguments) > 0:
raise ValueError(f"Got unexpected arguments: {deprecated_arguments}")
return_dict = return_dict if return_dict is not None else self.config.use_return_dict
transformer_outputs = self.transformer(
input_ids,
past_key_values=past_key_values,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
head_mask=head_mask,
inputs_embeds=inputs_embeds,
use_cache=use_cache,
output_attentions=output_attentions,
output_hidden_states=output_hidden_states,
return_dict=return_dict,
)
hidden_states = transformer_outputs[0]
lm_logits = self.lm_head(hidden_states)
loss = None
if labels is not None:
# Shift so that tokens < n predict n
shift_logits = lm_logits[..., :-1, :].contiguous()
shift_labels = labels[..., 1:].contiguous()
batch_size, seq_length, vocab_size = shift_logits.shape
# Flatten the tokens
loss_fct = CrossEntropyLoss()
loss = loss_fct(
shift_logits.view(batch_size * seq_length, vocab_size), shift_labels.view(batch_size * seq_length)
)
if not return_dict:
output = (lm_logits,) + transformer_outputs[1:]
return ((loss,) + output) if loss is not None else output
return CausalLMOutputWithCrossAttentions(
loss=loss,
logits=lm_logits,
past_key_values=transformer_outputs.past_key_values,
hidden_states=transformer_outputs.hidden_states,
attentions=transformer_outputs.attentions,
)
def _reorder_cache(
self, past: Tuple[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor], ...], beam_idx: torch.LongTensor
) -> Tuple[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor], ...]:
"""
This function is used to re-order the `past_key_values` cache if [`~PreTrainedModel.beam_search`] or
[`~PreTrainedModel.beam_sample`] is called. This is required to match `past_key_values` with the correct
beam_idx at every generation step.
Output shares the same memory storage as `past`.
"""
standardized_past = self._convert_to_standard_cache(past, batch_size=len(beam_idx))
# Get a copy of `beam_idx` on all the devices where we need those indices.
device_to_beam_idx = {
past_state.device: beam_idx.to(past_state.device) for layer_past in past for past_state in layer_past
}
reordered_past = tuple(
(
layer_past[0].index_select(0, device_to_beam_idx[layer_past[0].device]),
layer_past[1].index_select(0, device_to_beam_idx[layer_past[0].device]),
)
for layer_past in standardized_past
)
return self._convert_to_rw_cache(reordered_past)
class RWForSequenceClassification(RWPreTrainedModel):
_keys_to_ignore_on_load_missing = [r"h.*.self_attention.scale_mask_softmax.causal_mask", r"lm_head.weight"]
def __init__(self, config: RWConfig):
super().__init__(config)
self.num_labels = config.num_labels
self.transformer = RWModel(config)
self.score = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, config.num_labels, bias=False)
# Initialize weights and apply final processing
self.post_init()
def forward(
self,
input_ids: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
past_key_values: Optional[Tuple[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor], ...]] = None,
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
head_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
inputs_embeds: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
labels: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
use_cache: Optional[bool] = None,
output_attentions: Optional[bool] = None,
output_hidden_states: Optional[bool] = None,
return_dict: Optional[bool] = None,
**deprecated_arguments,
) -> Union[Tuple[torch.Tensor], SequenceClassifierOutputWithPast]:
r"""
labels (`torch.LongTensor` of shape `(batch_size,)`, *optional*):
Labels for computing the sequence classification/regression loss. Indices should be in `[0, ...,
config.num_labels - 1]`. If `config.num_labels == 1` a regression loss is computed (Mean-Square loss), If
`config.num_labels > 1` a classification loss is computed (Cross-Entropy).
"""
if deprecated_arguments.pop("position_ids", False) is not False:
# `position_ids` could have been `torch.Tensor` or `None` so defaulting pop to `False` allows to detect if users were passing explicitly `None`
warnings.warn(
"`position_ids` have no functionality in BLOOM and will be removed in v5.0.0. You can safely ignore"
" passing `position_ids`.",
FutureWarning,
)
if len(deprecated_arguments) > 0:
raise ValueError(f"Got unexpected arguments: {deprecated_arguments}")
return_dict = return_dict if return_dict is not None else self.config.use_return_dict
transformer_outputs = self.transformer(
input_ids,
past_key_values=past_key_values,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
head_mask=head_mask,
inputs_embeds=inputs_embeds,
use_cache=use_cache,
output_attentions=output_attentions,
output_hidden_states=output_hidden_states,
return_dict=return_dict,
)
hidden_states = transformer_outputs[0]
logits = self.score(hidden_states)
if input_ids is not None:
batch_size = input_ids.shape[0]
else:
batch_size = inputs_embeds.shape[0]
if self.config.pad_token_id is None and batch_size != 1:
raise ValueError("Cannot handle batch sizes > 1 if no padding token is defined.")
if self.config.pad_token_id is None:
sequence_lengths = -1
else:
if input_ids is not None:
sequence_lengths = torch.ne(input_ids, self.config.pad_token_id).sum(dim=-1) - 1
else:
sequence_lengths = -1
logger.warning(
f"{self.__class__.__name__} will not detect padding tokens in `inputs_embeds`. Results may be "
"unexpected if using padding tokens in conjunction with `inputs_embeds.`"
)
pooled_logits = logits[torch.arange(batch_size, device=logits.device), sequence_lengths]
loss = None
if labels is not None:
if self.config.problem_type is None:
if self.num_labels == 1:
self.config.problem_type = "regression"
elif self.num_labels > 1 and (labels.dtype == torch.long or labels.dtype == torch.int):
self.config.problem_type = "single_label_classification"
else:
self.config.problem_type = "multi_label_classification"
if self.config.problem_type == "regression":
loss_fct = MSELoss()
if self.num_labels == 1:
loss = loss_fct(pooled_logits.squeeze(), labels.squeeze())
else:
loss = loss_fct(pooled_logits, labels)
elif self.config.problem_type == "single_label_classification":
loss_fct = CrossEntropyLoss()
loss = loss_fct(pooled_logits, labels)
elif self.config.problem_type == "multi_label_classification":
loss_fct = BCEWithLogitsLoss()
loss = loss_fct(pooled_logits, labels)
if not return_dict:
output = (pooled_logits,) + transformer_outputs[1:]
return ((loss,) + output) if loss is not None else output
return SequenceClassifierOutputWithPast(
loss=loss,
logits=pooled_logits,
past_key_values=transformer_outputs.past_key_values,
hidden_states=transformer_outputs.hidden_states,
attentions=transformer_outputs.attentions,
)
class RWForTokenClassification(RWPreTrainedModel):
_keys_to_ignore_on_load_missing = [r"h.*.self_attention.scale_mask_softmax.causal_mask", r"lm_head.weight"]
def __init__(self, config: RWConfig):
super().__init__(config)
self.num_labels = config.num_labels
self.transformer = RWModel(config)
if hasattr(config, "classifier_dropout") and config.classifier_dropout is not None:
classifier_dropout = config.classifier_dropout
elif hasattr(config, "hidden_dropout") and config.hidden_dropout is not None:
classifier_dropout = config.hidden_dropout
else:
classifier_dropout = 0.1
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(classifier_dropout)
self.classifier = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, config.num_labels)
# Initialize weights and apply final processing
self.post_init()
def forward(
self,
input_ids: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
past_key_values: Optional[Tuple[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor], ...]] = None,
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
head_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
inputs_embeds: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
labels: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
use_cache: Optional[bool] = None,
output_attentions: Optional[bool] = None,
output_hidden_states: Optional[bool] = None,
return_dict: Optional[bool] = None,
**deprecated_arguments,
) -> Union[Tuple[torch.Tensor], TokenClassifierOutput]:
r"""
labels (`torch.LongTensor` of shape `(batch_size,)`, *optional*):
Labels for computing the sequence classification/regression loss. Indices should be in `[0, ...,
config.num_labels - 1]`. If `config.num_labels == 1` a regression loss is computed (Mean-Square loss), If
`config.num_labels > 1` a classification loss is computed (Cross-Entropy).
"""
if deprecated_arguments.pop("position_ids", False) is not False:
# `position_ids` could have been `torch.Tensor` or `None` so defaulting pop to `False` allows to detect if users were passing explicitly `None`
warnings.warn(
"`position_ids` have no functionality in BLOOM and will be removed in v5.0.0. You can safely ignore"
" passing `position_ids`.",
FutureWarning,
)
if len(deprecated_arguments) > 0:
raise ValueError(f"Got unexpected arguments: {deprecated_arguments}")
return_dict = return_dict if return_dict is not None else self.config.use_return_dict
transformer_outputs = self.transformer(
input_ids,
past_key_values=past_key_values,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
head_mask=head_mask,
inputs_embeds=inputs_embeds,
use_cache=use_cache,
output_attentions=output_attentions,
output_hidden_states=output_hidden_states,
return_dict=return_dict,
)
hidden_states = transformer_outputs[0]
hidden_states = self.dropout(hidden_states)
logits = self.classifier(hidden_states)
loss = None
if labels is not None:
batch_size, seq_length = labels.shape
loss_fct = CrossEntropyLoss()
loss = loss_fct(logits.view(batch_size * seq_length, self.num_labels), labels.view(batch_size * seq_length))
if not return_dict:
output = (logits,) + transformer_outputs[2:]
return ((loss,) + output) if loss is not None else output
return TokenClassifierOutput(
loss=loss,
logits=logits,
hidden_states=transformer_outputs.hidden_states,
attentions=transformer_outputs.attentions,
)
class RWForQuestionAnswering(RWPreTrainedModel):
_keys_to_ignore_on_load_missing = [r"h.*.self_attention.scale_mask_softmax.causal_mask", r"lm_head.weight"]
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__(config)
self.transformer = RWModel(config)
self.qa_outputs = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, 2)
# Initialize weights and apply final processing
self.post_init()
def forward(
self,
input_ids: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
attention_mask: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
position_ids: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
head_mask: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
inputs_embeds: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
start_positions: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
end_positions: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
output_attentions: Optional[bool] = None,
output_hidden_states: Optional[bool] = None,
return_dict: Optional[bool] = None,
) -> Union[Tuple, QuestionAnsweringModelOutput]:
r"""
start_positions (`torch.LongTensor` of shape `(batch_size,)`, *optional*):
Labels for position (index) of the start of the labelled span for computing the token classification loss.
Positions are clamped to the length of the sequence (`sequence_length`). Position outside of the sequence
are not taken into account for computing the loss.
end_positions (`torch.LongTensor` of shape `(batch_size,)`, *optional*):
Labels for position (index) of the end of the labelled span for computing the token classification loss.
Positions are clamped to the length of the sequence (`sequence_length`). Position outside of the sequence
are not taken into account for computing the loss.
"""
return_dict = return_dict if return_dict is not None else self.config.use_return_dict
outputs = self.transformer(
input_ids,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
position_ids=position_ids,
head_mask=head_mask,
inputs_embeds=inputs_embeds,
output_attentions=output_attentions,
output_hidden_states=output_hidden_states,
return_dict=return_dict,
)
sequence_output = outputs[0]
logits = self.qa_outputs(sequence_output)
start_logits, end_logits = logits.split(1, dim=-1)
start_logits = start_logits.squeeze(-1).contiguous()
end_logits = end_logits.squeeze(-1).contiguous()
total_loss = None
if start_positions is not None and end_positions is not None:
# If we are on multi-GPU, split add a dimension
if len(start_positions.size()) > 1:
start_positions = start_positions.squeeze(-1)
if len(end_positions.size()) > 1:
end_positions = end_positions.squeeze(-1)
# sometimes the start/end positions are outside our model inputs, we ignore these terms
ignored_index = start_logits.size(1)
start_positions = start_positions.clamp(0, ignored_index)
end_positions = end_positions.clamp(0, ignored_index)
loss_fct = CrossEntropyLoss(ignore_index=ignored_index)
start_loss = loss_fct(start_logits, start_positions)
end_loss = loss_fct(end_logits, end_positions)
total_loss = (start_loss + end_loss) / 2
if not return_dict:
output = (start_logits, end_logits) + outputs[2:]
return ((total_loss,) + output) if total_loss is not None else output
return QuestionAnsweringModelOutput(
loss=total_loss,
start_logits=start_logits,
end_logits=end_logits,
hidden_states=outputs.hidden_states,
attentions=outputs.attentions,
)Join the The State of AI Newsletter
Every week, receive a curated collection of cutting-edge AI developments, practical tutorials, and analysis, empowering you to stay ahead in the rapidly evolving field of AI.
I won't send you any spam, ever!